In this course, you’ll explore three exploratory data analysis (EDA) practices: cleaning, joining, and validating. You'll discover the importance of these practices for data analysis, and you’ll use Python to clean, validate, and join data.

Clean Your Data

Clean Your Data
Ce cours fait partie de Spécialisation "Google Data Analysis with Python"

Instructeur : Google Career Certificates
Inclus avec
19 avis
Ce que vous apprendrez
Explore the EDA practices of cleaning, validating and joining data
Compétences que vous acquerrez
- Catégorie : Data Integration
- Catégorie : Data Preprocessing
Détails à connaître

Ajouter à votre profil LinkedIn
septembre 2025
5 devoirs
Découvrez comment les employés des entreprises prestigieuses maîtrisent des compétences recherchées

Élaborez votre expertise du sujet
- Apprenez de nouveaux concepts auprès d'experts du secteur
- Acquérez une compréhension de base d'un sujet ou d'un outil
- Développez des compétences professionnelles avec des projets pratiques
- Obtenez un certificat professionnel partageable

Il y a 5 modules dans ce cours
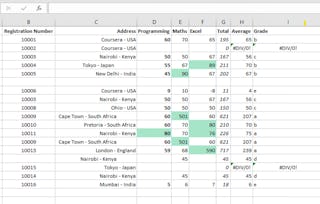
Missing or duplicate data can appear in datasets for numerous reasons. The impact of missing values can vary depending on how many are present. In this module, you will learn strategies to address missing data entries, determine when deduplication is needed, and use common Python functions for handling duplicates.
Inclus
4 vidéos1 lecture1 devoir3 laboratoires non notés
Outliers are data points that stand out amongst others. A tactful approach to outliers recognizes the human stories and real-world effects they represent. In this module, you will learn the types of outliers, how to handle them, and visualize them.
Inclus
2 vidéos2 lectures1 devoir
Data models typically work better with numerical inputs. To facilitate this, categorical data is encoded into numeric digits for analysis. In this module, you will learn why this transformation is needed, what dummy variables are, and how to select the right encoding method.
Inclus
2 vidéos2 lectures1 devoir
Input validation focuses on thoroughly checking data for completeness and to eliminate errors. In this module, you will learn why validation minimizes errors, how to detect improper inputs, and why it's essential for joining datasets.
Inclus
2 vidéos1 devoir2 laboratoires non notés1 plugin
Review everything you’ve learned and take the final assessment.
Inclus
1 lecture1 devoir
Obtenez un certificat professionnel
Ajoutez ce titre à votre profil LinkedIn, à votre curriculum vitae ou à votre CV. Partagez-le sur les médias sociaux et dans votre évaluation des performances.
Instructeur

Offert par
En savoir plus sur Data Analysis
 Statut : Essai gratuit
Statut : Essai gratuit Statut : Essai gratuit
Statut : Essai gratuitGoogle
Pour quelles raisons les étudiants sur Coursera nous choisissent-ils pour leur carrière ?

Felipe M.

Jennifer J.

Larry W.

Chaitanya A.
Avis des étudiants
- 5 stars
100 %
- 4 stars
0 %
- 3 stars
0 %
- 2 stars
0 %
- 1 star
0 %
Affichage de 3 sur 19
Révisé le 20 nov. 2025
From the Python course, I learned the foundational skills of programming, such as writing code, using variables, loops, and functions, and understanding how to solve problems using Python.”
Révisé le 15 déc. 2025
his course helped me understand the basics clearly and improved my practical skills. Well structured and easy to follow.

Ouvrez de nouvelles portes avec Coursera Plus
Accès illimité à 10,000+ cours de niveau international, projets pratiques et programmes de certification prêts à l'emploi - tous inclus dans votre abonnement.
Faites progresser votre carrière avec un diplôme en ligne
Obtenez un diplôme auprès d’universités de renommée mondiale - 100 % en ligne
Rejoignez plus de 3 400 entreprises mondiales qui ont choisi Coursera pour les affaires
Améliorez les compétences de vos employés pour exceller dans l’économie numérique
Foire Aux Questions
Organizations of all types and sizes have business processes that generate massive volumes of data. Every moment, all sorts of information gets created by computers, the internet, phones, texts, streaming video, photographs, sensors, and much more. In the global digital landscape, data is increasingly imprecise, chaotic, and unstructured. As the speed and variety of data increases exponentially, organizations are struggling to keep pace.
Data science is part of a field of study that uses raw data to create new ways of modeling and understanding the unknown. To gain insights, businesses rely on data professionals to acquire, organize, and interpret data, which helps inform internal projects and processes. Data scientists rely on a combination of critical skills, including statistics, scientific methods, data analysis, and artificial intelligence.
A data professional is a term used to describe any individual who works with data and/or has data skills. At a minimum, a data professional is capable of exploring, cleaning, selecting, analyzing, and visualizing data. They may also be comfortable with writing code and have some familiarity with the techniques used by statisticians and machine learning engineers, including building models, developing algorithmic thinking, and building machine learning models.
Data professionals are responsible for collecting, analyzing, and interpreting large amounts of data within a variety of different organizations. The role of a data professional is defined differently across companies. Generally speaking, data professionals possess technical and strategic capabilities that require more advanced analytical skills such as data manipulation, experimental design, predictive modeling, and machine learning. They perform a variety of tasks related to gathering, structuring, interpreting, monitoring, and reporting data in accessible formats, enabling stakeholders to understand and use data effectively. Ultimately, the work of data professionals helps organizations make informed, ethical decisions.
Large volumes of data — and the technology needed to manage and analyze it — are becoming increasingly accessible. Because of this, there has been a surge in career opportunities for people who can tell stories using data, such as senior data analysts and data scientists. These professionals collect, analyze, and interpret large amounts of data within a variety of different organizations. Their responsibilities require advanced analytical skills such as data manipulation, experimental design, predictive modeling, and machine learning.
Plus de questions
Aide financière disponible,