This course introduces statistical inference, sampling distributions, and confidence intervals. Students will learn how to define and construct good estimators, method of moments estimation, maximum likelihood estimation, and methods of constructing confidence intervals that will extend to more general settings.

Statistical Estimation for Data Science and AI
Seize the savings! Get 40% off 3 months of Coursera Plus and full access to thousands of courses.

Statistical Estimation for Data Science and AI
This course is part of multiple programs.

Instructor: Jem Corcoran
9,445 already enrolled
Included with
89 reviews
Recommended experience
What you'll learn
Identify characteristics of “good” estimators and be able to compare competing estimators.
Construct sound estimators using the techniques of maximum likelihood and method of moments estimation.
Construct and interpret confidence intervals for one and two population means, one and two population proportions, and a population variance.
Details to know

Add to your LinkedIn profile
2 quizzes, 11 assignments
See how employees at top companies are mastering in-demand skills

Build your subject-matter expertise
- Learn new concepts from industry experts
- Gain a foundational understanding of a subject or tool
- Develop job-relevant skills with hands-on projects
- Earn a shareable career certificate

There are 6 modules in this course
Earn a career certificate
Add this credential to your LinkedIn profile, resume, or CV. Share it on social media and in your performance review.
Build toward a degree
This course is part of the following degree program(s) offered by University of Colorado Boulder. If you are admitted and enroll, your completed coursework may count toward your degree learning and your progress can transfer with you.¹
Instructor

Offered by
Explore more from Probability and Statistics
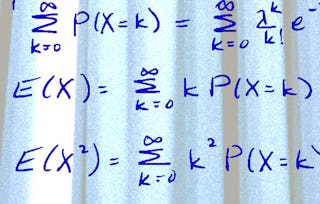 Status: Free Trial
Status: Free TrialUniversity of Colorado Boulder
 Status: Free Trial
Status: Free TrialUniversity of Colorado Boulder
University of Colorado Boulder
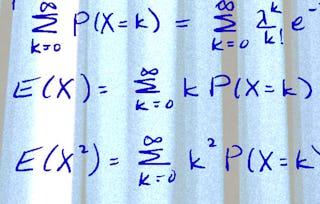 Status: Free Trial
Status: Free TrialUniversity of Colorado Boulder
Why people choose Coursera for their career

Felipe M.

Jennifer J.

Larry W.

Chaitanya A.
Learner reviews
- 5 stars
58.42%
- 4 stars
17.97%
- 3 stars
6.74%
- 2 stars
6.74%
- 1 star
10.11%
Showing 3 of 89
Reviewed on Jul 18, 2024
This course provided me with truly deep insights into the inner workings of statistics. Thank you very much.
Reviewed on Sep 3, 2022
The instrustor, Dr. Jem, is really interesting. She made the hard part of the Statistics easy to understand!
Reviewed on Jan 27, 2024
Excellent. Challenging quizzes that really make you apply the points from the lectures. Very detailed course that has taken me to the next level of my understanding of statistical inference.

Open new doors with Coursera Plus
Unlimited access to 10,000+ world-class courses, hands-on projects, and job-ready certificate programs - all included in your subscription
Advance your career with an online degree
Earn a degree from world-class universities - 100% online
Join over 3,400 global companies that choose Coursera for Business
Upskill your employees to excel in the digital economy