Work Breakdown Structure (WBS): Overview, Uses, and Software
Learn what a work breakdown structure (WBS) is, when it's used, the types of WBS, and how to use this project management tool.
![[Featured image] A project manager is standing in front of a board with documents in one hand and a pen in the other. They're with their coworker discussing the work breakdown structure.](https://d3njjcbhbojbot.cloudfront.net/api/utilities/v1/imageproxy/https://images.ctfassets.net/wp1lcwdav1p1/268InHw2GVvODLFB59EZu7/2b4b909bcfe4afd018dac489b0745d34/GettyImages-502359618__3_.jpg?w=1500&h=680&q=60&fit=fill&f=faces&fm=jpg&fl=progressive&auto=format%2Ccompress&dpr=1&w=1000)
A well-defined work breakdown structure (WBS) is an essential tool for project managers in any industry. A WBS breaks down large projects into bite-sized pieces, making it easier to plan, schedule, track progress, and identify potential roadblocks.
Use this guide to explore WBS and its various applications in ensuring successful project completion. Discover how WBS decomposes complex projects into manageable components, facilitating planning, scheduling, risk identification, and overall project clarity.
If you're ready to kickstart your career in project management, enrolling in the University of Colorado's Project Management Specialization is a good place to start. This Specialization introduces core project management principles, covering leadership, team roles, budgeting, scheduling, risk, quality, and the full project lifecycle.
What is a work breakdown structure?
A work breakdown structure (WBS) is a project management tool that decomposes the total work required to deliver a product, service, or project into smaller, more manageable components. A WBS provides a hierarchical view of your project’s scope, translating overall strategies and objectives into specific goals, workflows, project phases, and action plans.
What is the purpose of a work breakdown structure?
In project management, you’ll use work breakdown structures for several reasons:
To identify the project tasks that make up the critical path of your project
To schedule activities that comprise the performance measurement baseline (PMB)
To define the deliverables for your project
To plan your resources, timelines, and priorities
To get a clearer picture of the risks the project may face as it progresses
Project planning, scheduling, and budgeting
The top level of your WBS represents the project's final deliverable, or end product. It represents the project scope statement. The lower levels break down the scope into more detailed deliverables and individual tasks. All these sub-elements can have time and cost estimates associated with them. When combined, they form a total estimate of what’s required for the project team to complete the project within its defined scope. This makes it possible for you to plan, schedule, and form budgets based on the details of the project rather than relying on high-level guesstimates.
Risk management, resource management, task management, and team management
The work breakdown structure lets you dissect the project to understand how it all fits together and create a Gantt chart that provides clear focus and critical path requirements.
When you create a WBS, you’re required to think through each activity in detail to define all the work necessary to complete it. In doing so, you’ll identify risks that may impact your project. These can go on the risk register, and you can then form an appropriate project risk plan.
You will also identify the resources needed to complete each task, which will help you plan how many people you need on your team and when you need them. This will help you manage your team during the project life cycle because you can assign each task to a team member with the required expertise.
Learn more: What Is a RACI Chart?
Benefits of using a work breakdown structure
A work breakdown structure offers several advantages throughout the project lifecycle. It can foster improved communication, task clarity, time estimation accuracy, risk mitigation, and efficient resource allocation within your project team.
Better communication with your team members regarding tasks
Clearer definition of the deliverables that need to be produced during each project stage
More accurate time estimates for each task because you can see precisely what needs to be done for each step of the project
Easier identification of critical path items, so you can take steps to reduce risks to these tasks (e.g., add resources or assign another team member to help complete them)
Easier identification of which tasks should be done by whom, because you can see where the expertise is needed most
Work breakdown structure examples: Types of WBS
You can use different types of work breakdown structures to define deliverables and schedule tasks:
1. Process-oriented WBS
A process-oriented WBS decomposes work into the processes needed to accomplish it, such as requirements, design, development, and testing. This type of breakdown structure has the advantage of clarifying tasks and assigning task owners. It also makes it easy to assign resources and estimate time because they can be assigned at each level of the structure. Process-oriented WBS provides clear milestones and is thus often preferred by clients.
2. Phase-based work breakdown structure
Similar to a process-oriented WBS, a phase-based WBS is a project management approach that breaks projects down into phases, each of which has its own purpose and features. The phases are usually broken down into smaller tasks, which are typically broken down even further into simpler tasks.
3. Deliverable-oriented WBS
A deliverable-oriented WBS is a hierarchical tree structure of the project and its components. It decomposes work into tangible products or services, such as database schema and user manuals. It shows the connection between the high-level deliverables and the work to be done. The deliverable-based WBS organizes the work horizontally as related activities, providing a view of the entire project from start to finish.
The advantage of this type of breakdown structure is that it gives an overview of the deliverables required for a project. This type of WBS is most appreciated by project teams and management.
4. Resource breakdown structure
The resource breakdown structure (RBS) is used to identify all of the resources required to complete each work package in the WBS and for the project. It can be developed by starting with the work packages in the WBS, then collecting all of the resources needed to complete each work package, and finally organizing them into a hierarchical structure based on their similarity or specialty.
The goal of the RBS is to ensure that all necessary resources are available to carry out the project and that there are no conflicts in their usage, which could delay the project.
5. Risk breakdown structure
A risk breakdown structure (RBS) is used to organize risks into categories and subcategories in a way that helps you manage them effectively. Risk categories may be defined by type, risk source, or other means deemed appropriate for your project.
A risk category would be something like cost, schedule, quality, or scope. Risk subcategories would be more specific risk types within each category. For example, under cost risks, you might have subcategories like labor rates, material costs, or budget overruns.
6. Cost breakdown structure
A cost breakdown structure (CBS) shows the estimated cost of each project element. For example, the cost of a website includes hosting, programming, design, and content creation. The CBS makes it easier to estimate a project budget and control costs.
7. Organizational breakdown structure
An organizational breakdown structure (OBS) shows how roles are assigned within an organization. For example, a medium-sized online business might have a chief technology officer, chief operating officer, chief executive officer, and other roles, each with different responsibilities.
What are the elements of work breakdown structure?
A work breakdown structure is comprised of several key components:
WBS dictionary: The WBS dictionary documents each component with its definition, estimated effort, and performance measurements. It allows you to define each step of the WBS and how it will be executed.
WBS levels: The WBS levels provide context for each portion of the project and determine the hierarchy of tasks and deliverables.
Project deliverables: Project deliverables are the desired outcomes of project tasks. They are grouped into work packages.
Work packages: A work package is the lowest level in the WBS. It represents the work needed to accomplish a specific deliverable. Work packages describe activities that can be planned, scheduled, and controlled by one person. Once completed, it should be possible to hand over the work package to another person.
Planning packages: Planning packages are used as an independent planning horizon for one or more work packages that will be completed in the future. They help to summarize the project plan at different levels.
Control accounts: Control accounts help control costs and schedules on projects with very large budgets or when a large part of the budget or duration applies to only one or two major deliverables. Control accounts function like work packages with some additional requirements. Control accounts are usually created for major parts of the project, such as phases and key deliverables.
Tasks: Tasks are work packages broken down into smaller activities so they can be scheduled, monitored, and controlled by one person.

How to create a work breakdown structure
A WBS helps everyone on the project team understand what needs to be completed, who's responsible for each task, how tasks relate to one another, when things should be done, and how much they will cost. Follow these steps to create a WBS.
1. Define the project scope.
Start by identifying the overall project goal, the deliverables, boundaries, and deadlines. What are the major outcomes that your team needs to achieve in order to complete the project? What does the project include and exclude?
2. Gather critical documents.
Gather critical documents, including:
Project management plan, outlining the project's execution, monitoring, scheduling, and resources.
Risk register, detailing potential risks and mitigation strategies.
Project scope statement, outlining the project's objectives, deliverables, and boundaries.
3. Create a hierarchy.
Organize the project into a hierarchical structure, with the major deliverables as the highest level.
4. Decompose project components.
Break down each deliverable into smaller, manageable tasks or work packages that can be assigned and tracked.
5. Identify key team members.
Determine the individual or team who'll be responsible for each task. This step will ensure accountability and help project team members communicate effectively.
6. Create the WBS dictionary.
After decomposition, create the WBS dictionary, which documents the project's key information, including the time and resources needed for each task and the relationships between them. The WBS dictionary can be represented as an outline or a diagram. Use boxes for each work package and lines to indicate the relationships between them.
7. Create a Gantt chart schedule.
After reviewing and validating the WBS thus far, create a Gantt chart schedule. The schedule is one of the most important components of a project management plan and will be used to monitor progress throughout the life of the project.
Work breakdown structure template
Here's a basic work breakdown structure template to give you an idea of how you can construct yours:
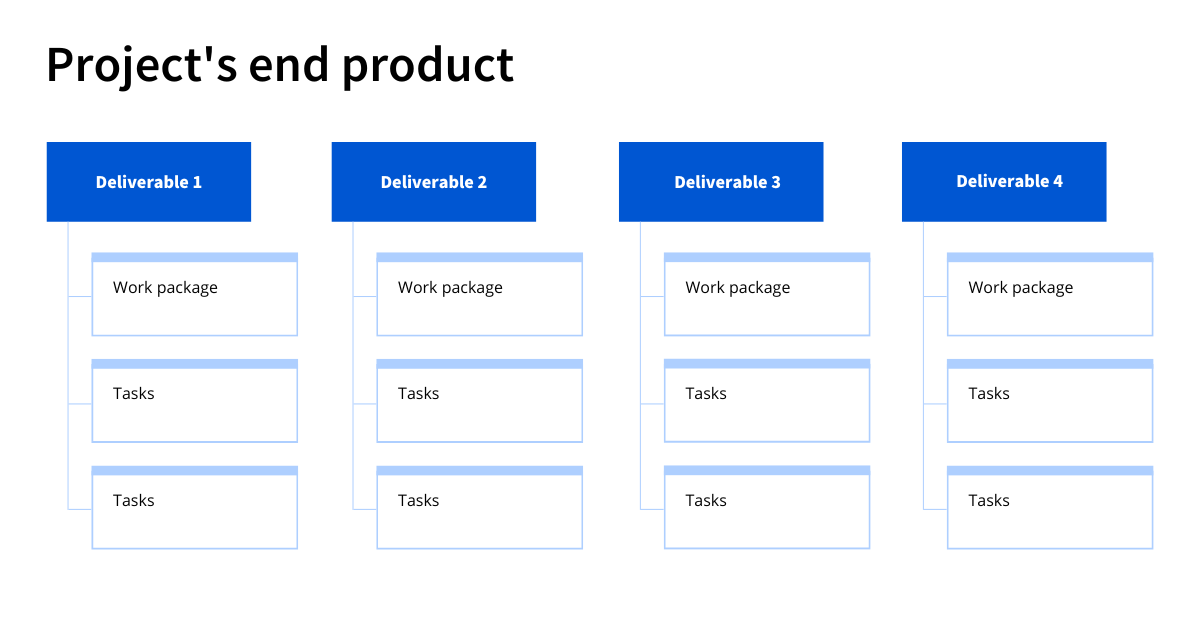
WBS software
A number of free and paid project management software programs are available to help you create a WBS for your projects. Before selecting a software tool, research a variety of them and evaluate their cost, features, and ease of use. Take a look at some common WBS software tools to get you started.
EdrawMax
EdrawMax is a versatile and capable diagramming application. It covers all aspects of WBS, from flowcharts to floor planning to business process diagrams. It's best suited for people who need a feature-rich tool that covers a wide variety of use cases.
Cost: Starts at $99 / year.
Lucidchart
Lucidchart is a cloud-based visual collaboration tool that allows teams to work together on the same diagram with real-time updates and live chat. Lucidchart provides a simple interface that enables you to create professional diagrams without prior experience.
Cost: Starts free.
SmartDraw
SmartDraw is a browser-based tool. It helps you draw flowcharts, organization charts, mind maps, project charts, and more. It’s useful for visualizing projects and individual aspects of a project.
Cost: Starts at $9.95 / month.
Visual Paradigm
Visual Paradigm is an extensive software suite that offers everything from project planning to source code management and test case design. This application is best suited for professional developers and managers working on large enterprise projects.
Cost: Starts at $6 / month.
MindView
MindView is designed specifically for project managers and business professionals who create mind maps to plan projects, brainstorm solutions, and present ideas visually. Mindview’s collaborative tools allow team members to work together on project planning.
Cost: Starts at $15 / month for a three-year subscription.
Creately
Creately is an online diagramming application that makes it easy to draw flowcharts, organizational charts, mind maps, and other diagrams online. Creately comes with features such as smart drawing aids that automatically align shapes while drawing flowcharts or other diagrams. You can also use it to collaborate with your colleagues in real time while working on a project together.
Cost: Starts free.
Stay in the loop with career trends and tips
Career growth is closer than you think. If you're considering a new career trajectory or looking to strengthen existing skills, then subscribe to our LinkedIn newsletter, Career Chat. You can also check out some of our free resources below:
Watch on YouTube: How to Become a Project Manager: 6 Essential Steps
Bookmark for tips: ChatGPT Prompt Sheet
Take a quiz: Career Test: What Career is Right for Me Quiz?
Drive your future career forward with a Coursera Plus subscription. When you enroll in either the monthly or annual option, you’ll gain access to over 10,000 courses—just check the course page to confirm your selection is included.
Frequently asked questions
The main reason project managers should use a WBS is to define the complete scope of a project in as much detail as possible. By doing this, you can assign work to your teams and break down their tasks further into actionable steps.
The best way for you to get started with a WBS is by defining your project's deliverables. What are the key things you want to create or accomplish? Once you have the deliverables defined, you can start breaking them down into individual phases, tasks, and subtasks until you have enough detail to allow your team members to perform the work required.
Coursera Staff
Editorial Team
Coursera’s editorial team is comprised of highly experienced professional editors, writers, and fact...
This content has been made available for informational purposes only. Learners are advised to conduct additional research to ensure that courses and other credentials pursued meet their personal, professional, and financial goals.
