Filter by
The language used throughout the course, in both instruction and assessments.
198 results for "geometry"

University of Colorado Boulder

University of Pennsylvania
Skills you'll gain: Estimation

University of Colorado Boulder
 Status: Free
Status: FreeDuke University

Johns Hopkins University
Skills you'll gain: Biostatistics, General Statistics, Probability & Statistics

Johns Hopkins University
Skills you'll gain: General Statistics, Probability & Statistics, Statistical Tests, Mathematics, Statistical Analysis, Biostatistics

Columbia University
Skills you'll gain: Computer Vision, Mathematics, Algebra, Algorithms, Computational Thinking, Linear Algebra

University of Colorado Boulder
Skills you'll gain: Computer Programming, Data Visualization, Programming Principles, R Programming, Statistical Programming, Computer Programming Tools, Data Structures, Data Analysis

Rice University
Skills you'll gain: Finance, Financial Analysis, Investment Management, Leadership and Management, Risk Management
 Status: Free
Status: FreeÉcole normale supérieure
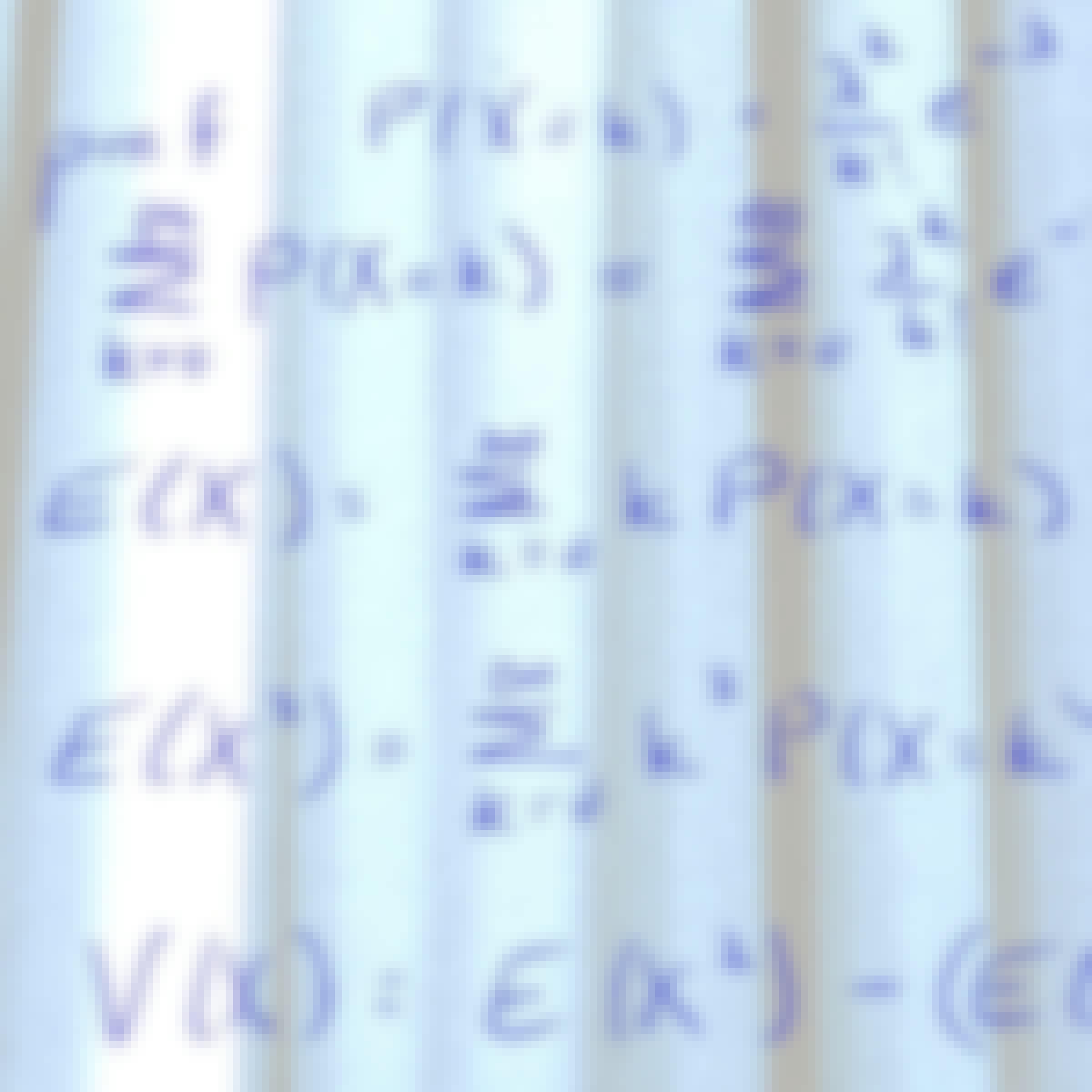
University of Colorado Boulder
Skills you'll gain: Probability & Statistics, General Statistics, Probability Distribution, Correlation And Dependence, Mathematics
 Status: Free
Status: FreePolitecnico di Milano
In summary, here are 10 of our most popular geometry courses
- Introduction to Computer Vision: University of Colorado Boulder
- Robotics: Estimation and Learning: University of Pennsylvania
- Spacecraft Formation Relative Orbits: University of Colorado Boulder
- Visual Perception and the Brain: Duke University
- Summary Statistics in Public Health : Johns Hopkins University
- Mathematical Biostatistics Boot Camp 2: Johns Hopkins University
- First Principles of Computer Vision: Columbia University
- Introduction to R Programming and Tidyverse: University of Colorado Boulder
- Investment Strategies and Portfolio Analysis: Rice University
- Approximation Algorithms Part II: École normale supérieure










